This Initiative – Initiative for Global Leadership in Concentrated Solar Power (CSP), focusing on 2 targets (a cost reduction target and an innovation target), was adopted in 2016 within the SET-Plan structures. A working group gathering representatives from several SET-Plan countries and the STE stakeholders from both industry and research sectors was set up to define a corresponding Implementation Plan (IP), which was officially adopted in June 2017, including 12 R&D action line and the implementation of new innovative, so-called First-Of-A-Kind (FOAK) plants.
FAQ
What is the Initiative about?
What is SET-Plan?
The SET-Plan is the technology pillar of the EU’s energy and climate policy
The Strategic energy Technology (SET) Plan, adopted by the European Union in 2008, is a first step to establish an energy technology policy for Europe. It is the principal decision-making support tool for European energy policy, with a goal of:
- Accelerating knowledge development, technology transfer and up-take;
- Maintaining EU industrial leadership on low-carbon energy technologies;
- Fostering science for transforming energy technologies to achieve the 2020 Energy and Climate Change goals;
- Contributing to the worldwide transition to a low carbon economy by 2050.
Implementation of the SET-Plan started with the establishment of the European Industrial Initiatives (EIIs) which bring together industry, the research community, the Member States and the Commission in risk-sharing, public-private partnerships aimed at the rapid development of key energy technologies at European level. In parallel, the European Energy Research Alliance (EERA) has been working since 2008 to align the R&D activities of individual research organisations to the needs of the SET-Plan priorities, and to establish a joint programming framework at the EU level. The projected budget for the SET-Plan has been estimated at up to €71.5 billion.
The SET-Plan has two major timelines
For 2020, the SET-Plan provides a framework to accelerate the development and deployment of cost-effective low carbon technologies. With such comprehensive strategies, the EU is on track to reach its 20-20-20 goals of a 20% reduction of CO2 emissions, a 20% share of energy from low-carbon energy sources and 20% reduction in the use of primary energy by improving energy efficiency by 2020.
For 2050, the SET-Plan is targeted at limiting climate change to a global temperature rise of no more than 2°C, in particular by matching the vision to reduce EU greenhouse gas emissions by 80 – 95%. The SET-Plan objective in this regard is to further lower the cost of low-carbon energy and put the EU’s energy industry at the forefront of the rapidly growing low-carbon energy technology sector.
What is SET-Plan IWG?
Implementation Working Group (IWG) of the SET-Plan gathering representatives from several SET-Plan countries the EC and the stakeholders (from both industry and research sectors) was set up in 2017 for carrying out the practical development of the Implementation Plan (IP) in order to achieve the “Initiative for Global Leadership in Concentrated Solar Power”.
The IWG on CSP/STE includes representatives of: Spain (Chair), Cyprus, France, Germany, Italy, Portugal, Turkey, the European Commission, the European Solar Thermal Electricity Association, the European Association of Gas and Steam Turbine Manufacturers and the Joint Programme on CSP/STE of the European Energy Research Alliance.
Implementation Plan is based on the guidance of the European Commission’s
Common Guiding Principles document, outlined by the SET-Plan Steering Committee.
The IP includes twelve strategic R&D activities and the implementation of an innovative CSP/STE plant, the so-called First-Of-A-Kind (FOAK) plant. Upon adoption of the Implementation Plan in June 2017, the TWG continued its tasks as “Implementation Working Group” (IWG) focusing from now on the concrete conditions for the implementation of the Initiative.
Why this project?
Since 2007, the initial deployment of solar thermal electricity (STE), also known as concentrated solar power (CSP), took place in Spain and brought the European STE sector spreading over ten EU countries to be a worldwide technology leader. But the further deployment has been hindered in Europe since 2013 due to retroactive changes in the investment conditions in Spain. To unlock this situation, the European Commission (EC) has launched in 2015 a dedicated Initiative – Initiative for Global Leadership in Concentrated Solar Power (CSP).
This resulted in an agreement between the EC and the CSP/STE sector on 2 targets (a cost reduction target and an innovation target). This Initiative was adopted in 2016 within the SET-Plan structures and a so-called Temporary Working Group (TWG) was set up gathering representatives from several SET-Plan countries, the EC and the stakeholders (from both industry and research sectors) to define a corresponding Implementation Plan (IP), which was officially adopted in June 2017. This IP includes twelve strategic R&D activities and the construction of innovative, known as First-Of-A-Kind (FOAK) CSP/STE plants. After the adoption of the IP, the TWG continued its tasks as an “Implementation Working Group” (IWG) to engineer the practical development of this Implementation Plan. In its H2020 Work Programme 2018-2020, the European Commission opened a call for Coordination and Support Action proposals that aim at supporting the execution of the a.m. initiatives, being aware that any decision (funding of R&I or defining the boundary conditions for energy technology choices and investments) is essentially a national competence.
What is this project going to do?
Acting as competence centre of the Implementation Working Group within the Strategic Energy Technology Plan (SET-Plan) of the European Commission, the overall goal of HORIZON-STE is to support the execution of the Implementation Plan regarding both STE/CSP Research and Innovation lines as well as First-Of-A-Kind projects that will help steer countries through political, legislative, and institutional shortcomings linked to various national policies concerning solar thermal electricity. Much of the focus centres on improving procurement of manageable RES and increased public funding for STE/CSP research.
This project will identify and address the relevant European countries, such as Spain, Italy, Germany, Turkey, France, the Netherlands, Luxembourg, Portugal, etc., having companies active in the global STE/CSP market, and/or as potential off-takers for STE/CSP generation in Europe.
Following the selection of relevant European countries for an efficient deployment of CSP/STE, HORIZON-STE, will propose solutions and pathways for overcoming the essential shortcomings of the current national strategies related to CSP/STE that are:
- for the industry: the legal framework conditions for procurement of manageable RES;
- for the R&I sector: entering in working relations with national funding agencies with the objective of extending to more public funding agencies and other sources the funding of R&I projects already ranked by all European CSP/STE stakeholders according to their expected impact on the sector. These projects were integrated in the Implementation Plan (IP).
These will result in national country reports and an EU-wide cooperation event that will be extensively covered by national mainstream media, supported by strong dissemination and a communication campaign throughout the whole project duration.
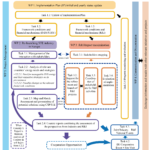
What is the current situation of the STE/CSP sector?
Since 2013, retroactive legislative and regulatory changes implemented in Spain hindered the further deployment of CSP/STE plants, the CSP/STE community (both industry companies and research centres closely cooperating within ESTELA) consistently pointed out that any initiative related to a re-launch of the CSP/STE market in Europe could only be realistically envisaged under one essential condition – a political initiative in at least one Member State that leads to:
- efficient funding instruments and blending solutions between various funding sources and instruments for R&D projects;
- new forms of calls for tenders from the industry related to new innovative CSP/STE plants in Europe that support the import of adequate amounts of dispatchable renewable energy, with the goals of:
- including in the generation portfolio a manageable technology (i.e. CSP/STE) with a proven ability to allow for a further increase of variable RES in a sustainable and affordable way;
- controlling the pathway to safely achieve its 2020 national RES targets as well as;
- delivering an efficient contribution to the EU RES targets by 2030 towards the target of a decarbonized EU power system by 2050;
- ensuring across EU the most efficient use of the existing natural resources;
- incentivising further CSP/STE research and maintaining the technology leadership held by Europe.
A significant part of the activities composing the project proposed is aimed at showcasing – in constructive dialogues between all involved stakeholders as close as possible to the political and market reality in selected Member States – the complementarity and coherence of measures needed by both the CSP/STE industry and its research community that should pave the way to any implementation strategy for the turn-around of the sector.
What is ERA-Nets?
European Research Area Networks (ERA-Nets) bring together predominantly European national funding agencies to provide a mechanism for the design and implementation of transnational activities. Of these activities, the most common is funding joint calls to facilitate collaborative research in specific themes.
The European Commission has funded ERA-Nets since 2003. In that time the instrument has taken on a number of different forms: ERA-Net, ERA-Net Plus and now, through Horizon 2020, ERA-Net Cofund. ERA-Nets serve to enhance collaboration while reducing fragmentation and duplication of effort across the European Research Area and beyond.
HORZION-STE takes an active role in ERA-Nets which are strategically important and provide the STE/CSP R&D community with opportunities to apply for funding for collaborative, transnational research in key areas.
What is ERA-Net Cofund scheme?
ERA-NET under Horizon 2020 is a funding instrument designed to support public-public partnerships in their
- preparation
- establishment of networking structures
- design and implementation
- coordination of joint activities
The instruments mainly ‘tops-up’ funding for single joint calls and transnational actions.
ERA-NET under Horizon 2020
The focus of ERA-NET has shifted from funding networks to ‘topping-up’ funding of single joint-calls for transnational research and innovation. This is done in selected areas with high European added-value and Horizon 2020 relevance.
ERA-NET under Horizon 2020 merges the former ERA-NET and ERA-NET Plus into a single financial instrument with the central compulsory element of implementing one substantial call with top-up funding from the Commission.
This aims to increase substantially the share of funding that Member States dedicate jointly to challenge driven research and innovation agendas.
Purpose of ERA-NET Cofund and difference from the former ERA-NET and ERA-NET Plus actions
ERA-NET Cofund under Horizon 2020 is a type of programme co-fund action designed to support public-public partnerships (P2Ps), including joint programming initiatives between Member States, in their preparation, establishment of networking structures, design, implementation and coordination of joint activities as well as Union topping-up of a trans-national call for proposals. It merges the former ERA-NET and ERA-NET Plus into a single instrument with the central and compulsory element of implementing one substantial call with top-up funding from the Commission. The focus of ERA-NETs is therefore shifting from the funding of networks to the top-up funding of single joint calls for transnational research and innovation in selected areas with high European added value and relevance for Horizon 2020. This aims at increasing substantially the share of funding that Member States dedicate jointly to challenge driven research and innovation agendas.
ERA-NETs based on Coordination and Support Action (CSA) are no longer possible. Only in exceptional cases it might be considered to support the preparation and structuring of specific emerging P2Ps that demonstrate clear European added value.

